Frequency inverters, commonly referred to as variable frequency drives (VFD), variable speed drives, or variable frequency inverters, are essential devices in modern industrial applications. They regulate the speed and torque of electric motors by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. Two primary control methods used in these devices are Vector Control and V/F Control. This article will delve into these control methods, explaining their concepts, features, and applications.

What Is Vector Control?
Vector Control, also known as field-oriented control (FOC), is a sophisticated control technique used in frequency inverters to manage the speed and torque of AC motors. It works by controlling the magnitude and phase of the motor current, allowing for precise regulation of motor performance.For instance, in an asynchronous motor, vector control derives magnetic flux equations, including those for stator flux, air gap flux, and rotor flux.
Detailed Explanation of Vector Control
Vector control concept
The core idea of vector control is to make an AC motor behave like a DC motor, achieving high-speed performance. This is done by decomposing the stator current vector of an asynchronous motor into a field current component and a torque current component. These components are controlled independently, maintaining their magnitude and phase. Vector control can be categorized into slip frequency control, sensorless vector control, and vector control with speed sensors.
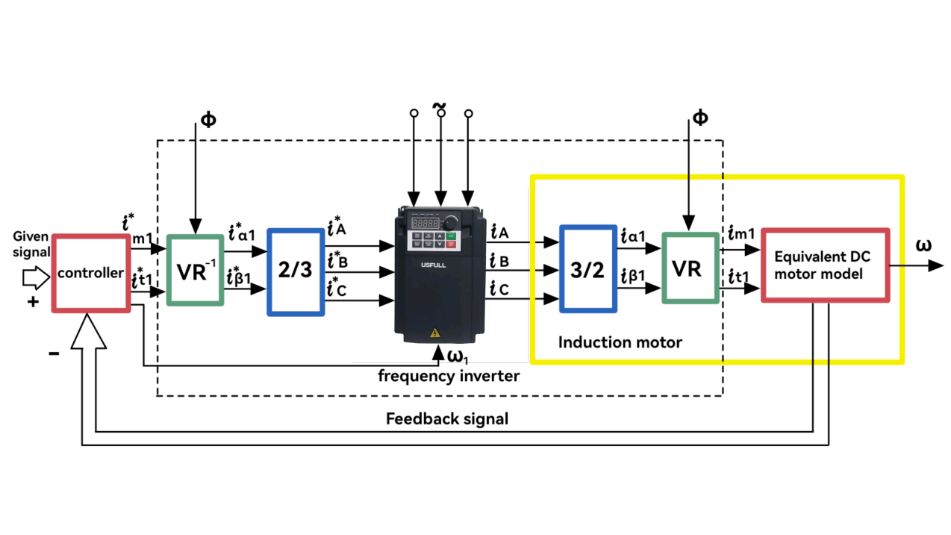
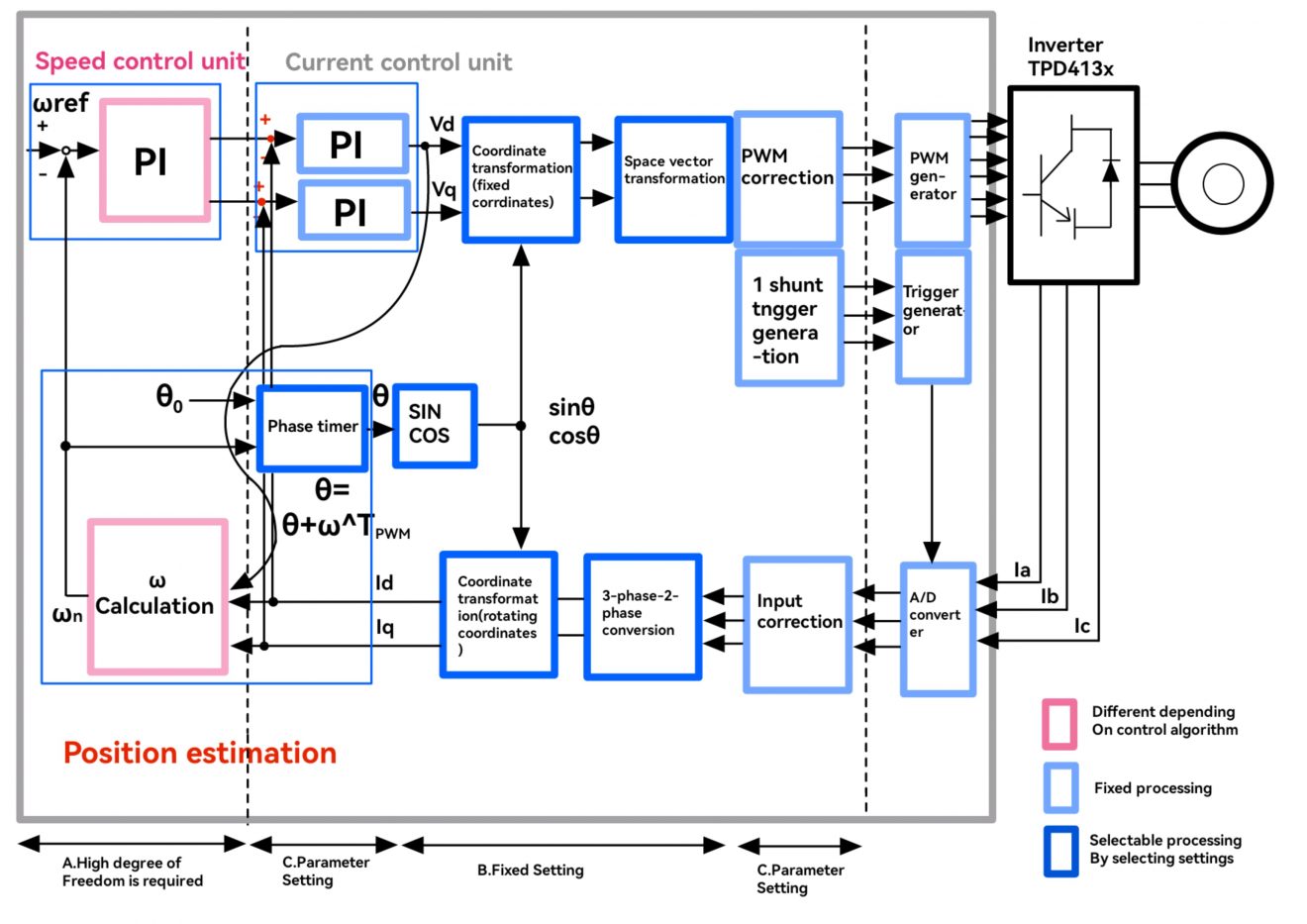
Vector control features
1.Non-feedback Vector Control:
Advantages:
- Easy to use without additional components.
- Stiff mechanical characteristics, avoiding magnetic circuit saturation.
Disadvantages:
- Limited speed range and dynamic response compared to feedback vector control.
2.Feedback Vector Control:
Advantages:
- Superior speed control performance.
Disadvantages:
- Requires installation of a speed sensor, increasing complexity and cost.
Application scope of vector control:
Vector Control is widely used in applications requiring high performance and precision, such as:
- CNC Machines:For accurate position and speed control.
- Robotics:Ensures smooth and precise movements.
- Elevators:Provides smooth and reliable operation.
- Industrial Washing Machines:Enhances control over washing cycles.
What Is V/F Control?
V/F Control, or Volts per Hertz control, is a simpler and more traditional method used in frequency inverters. It regulates the motor speed by maintaining a constant ratio between the voltage and frequency supplied to the motor.
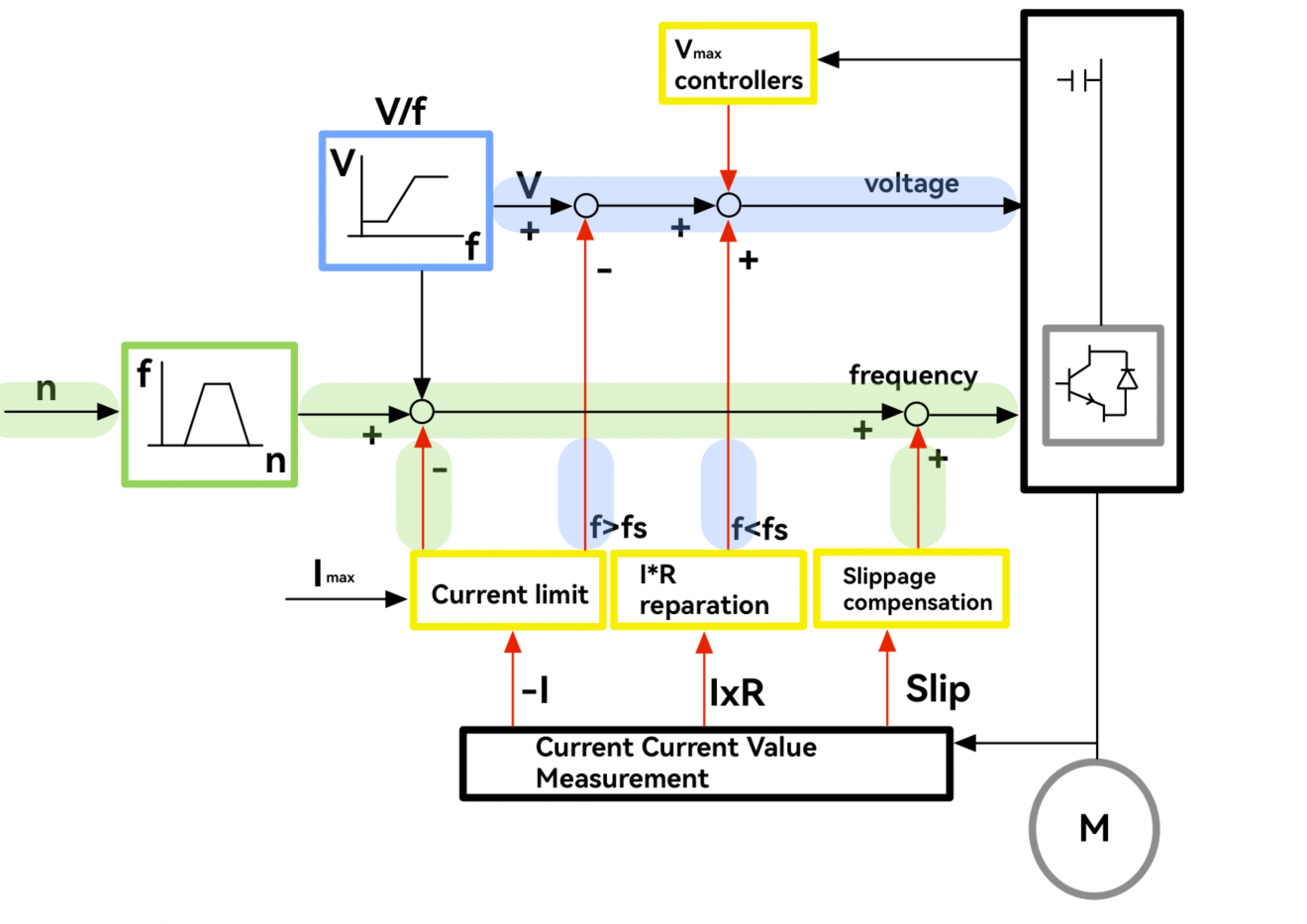
Detailed Explanation of V/F Control
Concept of V/F Control
The principle of V/F control is to change the voltage proportionally with the frequency. This keeps the motor’s magnetic flux constant, preventing weak magnetic fields and saturation. This control method is often preset in systems to ensure energy efficiency.
Comparison Between Vector Control and V/F Control
- Complexity:Vector control is complex, requiring advanced algorithms and sensors, while V/F control is simpler and easier to implement.
- Performance:Vector control offers superior performance, especially for dynamic and precision applications, whereas V/F control is sufficient for less demanding tasks.
- Cost:Vector control systems are generally more expensive due to their complexity.
- Efficiency:Vector control optimizes motor efficiency more effectively than V/F control.
In summary, the choice between Vector Control and V/F Control in a frequency inverter depends on the application’s specific requirements. Vector Control is ideal for high precision and dynamic performance applications, while V/F Control suits simpler, cost-sensitive applications where precise control is not as critical. Understanding these control methods allows industries to leverage the capabilities of variable frequency drives for enhanced motor performance and efficiency, leading to improved operational efficiency and productivity.




