What Are the Core Components of a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a motor controller that adjusts voltage and frequency to regulate motor speed and torque.
VFD consists of three main sections—rectifier/converter, DC bus, and inverter—ensuring precise control, energy efficiency, and extended motor life.
Let’s explore the critical components of VFDs, their functionality, and how they optimize motor control systems.

What Is a VFD Rectifier/Converter?
The rectifier/converter is the first stage of a VFD, responsible for converting incoming AC (alternating current) power into DC (direct current). This process is essential for providing a stable energy source for further processing within the VFD. It eliminates voltage fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance and protecting connected equipment from electrical surges.
What Is a VFD DC Bus?
The DC bus serves as an energy storage and distribution unit within a VFD. It smooths out the converted DC power, reducing ripples and ensuring stable voltage levels for the inverter stage. A well-designed DC bus improves efficiency, prevents energy loss, and provides backup power during brief interruptions, enhancing system reliability.
What Is a VFD Inverter?
The inverter converts DC power back into controlled AC power to regulate motor speed. By adjusting frequency and voltage output, the inverter provides precise speed control, reducing energy wastage and mechanical stress. This capability supports applications requiring variable speeds, making it ideal for pumps, fans, and conveyors.
What Is an IGBT in a VFD?
The Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a crucial switching device in VFDs. It manages the rapid on/off operations needed to generate variable AC output. IGBTs ensure high efficiency, low heat generation, and reliable performance, enabling smooth motor operation with minimal energy consumption and reduced noise levels.
What Is a VFD Ground?
A VFD ground establishes a safety path for excess electrical energy, preventing shocks and equipment damage. Proper grounding reduces electrical noise interference, protects sensitive components, and enhances compliance with safety regulations. Grounding systems are critical for maintaining stable operation and extending VFD lifespan.
What Is kW/hp in a VFD?
The kilowatt (kW) or horsepower (hp) rating defines a VFD’s power capacity. It determines the drive’s ability to handle motor loads. Selecting the correct kW/hp ensures optimal performance, prevents overheating, and accommodates application-specific requirements, whether for light-duty fans or heavy-duty compressors.
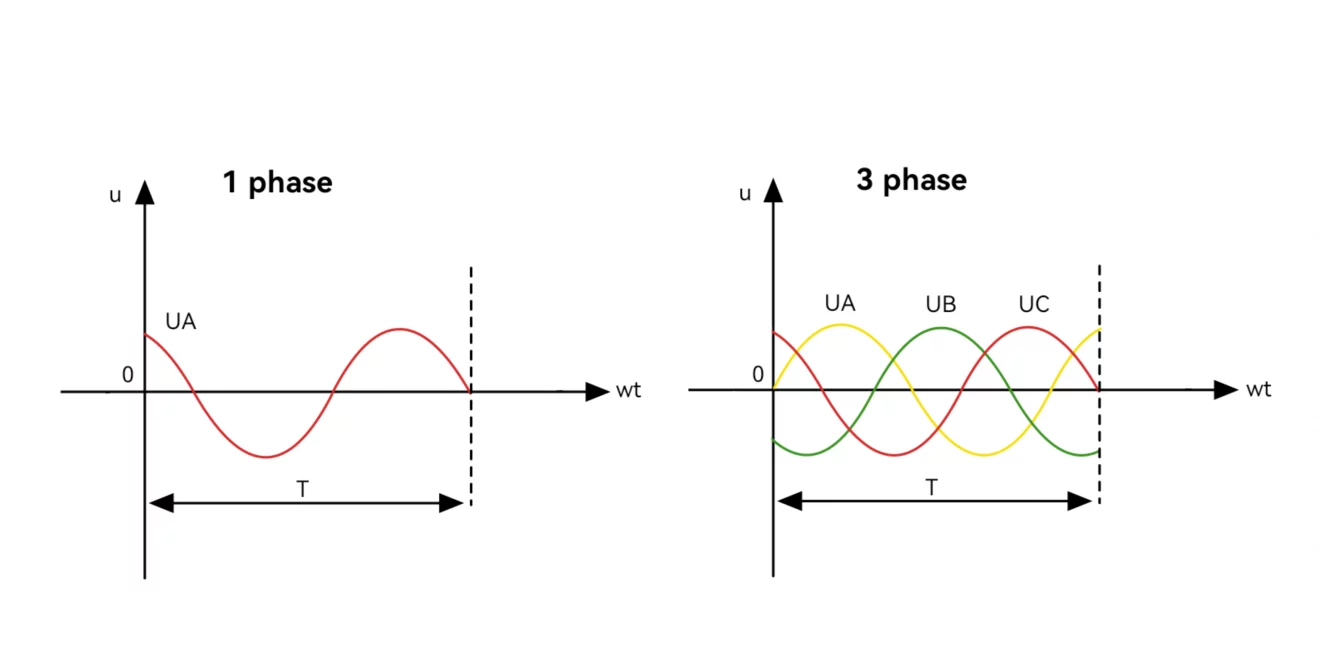
What Is Single-phase Power?
Single-phase power supplies energy through two wires (live and neutral), commonly used in residential or small commercial setups. VFDs designed for single-phase power cater to smaller motors, providing cost-effective solutions for low-power applications such as pumps and fans.
What Is Three-phase Power?
Three-phase power uses three alternating currents, delivering higher efficiency and stability. It’s ideal for industrial applications requiring substantial energy to operate large motors. VFDs compatible with three-phase systems optimize performance, minimize energy losses, and support seamless scalability for heavy-duty operations.
What Is a VFD Control Board?
The control board in a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) acts as its central processing unit, overseeing command execution, monitoring feedback, and running control algorithms. It processes input signals, adjusts settings, and ensures seamless operation across different load conditions. Advanced VFD control boards may also integrate programmable logic capabilities, enabling precise automation and diagnostics. In addition to the main control board, the power board works alongside, providing the necessary power management to support the drive’s functionality.

What Is a VFD Run Source?
A run source dictates how the VFD starts and controls motor operation—either locally (via a keypad) or remotely (via programmable logic controllers or sensors). Flexible run sources allow for tailored control systems, enhancing operational efficiency and adaptability in diverse industrial settings.
What Is a VFD Three-level Output?
A three-level output in a VFD improves waveform quality, reduces harmonic distortion, and enhances motor performance. By delivering smoother voltage transitions, it minimizes motor noise, reduces heat generation, and extends the lifespan of connected equipment, especially in high-power applications.
Power Efficiency Starts with Smart Control Systems.
Investing in a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) ensures optimized motor performance, energy savings, and operational reliability—empowering industries to achieve long-term sustainability.



