Variable frequency drives (VFDs) are essential for controlling motor speed, but without proper filtering, they can cause electrical noise, harmonics, and equipment damage. These issues lead to costly downtime and inefficiencies. The solution? Understanding and implementing the right input and output filters for your VFD system. Keep reading to discover the five critical filter types that can optimize your setup.
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) require input and output filters to mitigate electrical noise, harmonics, and equipment damage. Input filters include EMI filters, harmonic filters, and input reactors, while output filters consist of sine filters and output chokes. These filters ensure smoother operation, protect equipment, and improve energy efficiency in VFD systems.
Ready to dive deeper? Let’s explore the key input and output filters for VFDs and how they can enhance your system’s performance.
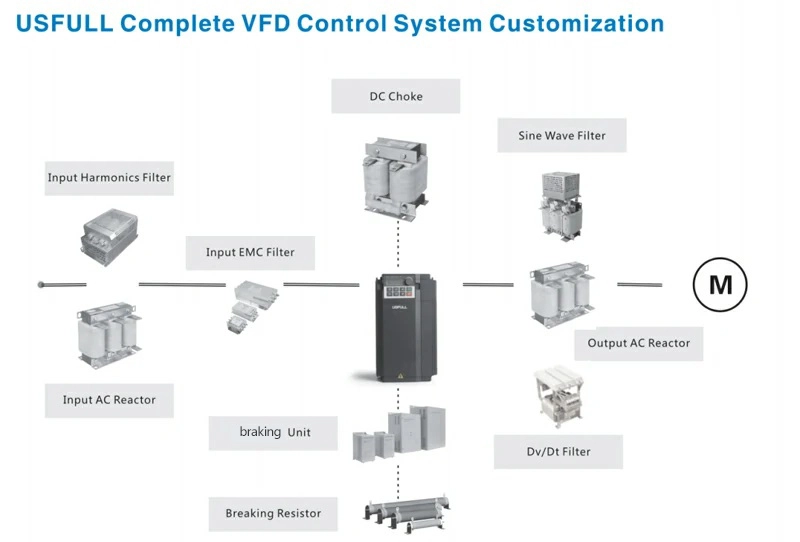
What Input Filters Are Available?
Input filters are crucial for protecting your variable frequency drive (VFD) from electrical disturbances originating from the power supply. They ensure stable operation and prevent damage to the VFD and connected equipment. Here are the three main types of input filters:

1. EMI Filter
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) filters are designed to suppress high-frequency noise generated by VFDs. This noise can disrupt other electronic devices and cause compliance issues with regulatory standards. EMI filters are installed at the input side of the VFD to block unwanted frequencies, ensuring cleaner power and reducing interference with nearby equipment.
2. Harmonic Filter
Harmonic filters address the distortion caused by non-linear loads in VFD systems. These distortions can overheat transformers, damage capacitors, and reduce overall system efficiency. Harmonic filters mitigate these issues by absorbing or canceling out harmonic currents, ensuring a smoother power supply and extending the lifespan of your equipment.
3. Input Reactor
Input reactors, also known as line reactors, are used to protect VFDs from voltage spikes and transient disturbances. They provide impedance to the input power supply, reducing the risk of damage caused by sudden voltage changes. Input reactors also help mitigate harmonics and improve the power factor, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
What Output Filters Are Available?
Output filters are equally important, as they protect the motor and other downstream equipment from the high-frequency switching noise generated by the VFD. Here are the two primary types of output filters:
1. Sine Filter
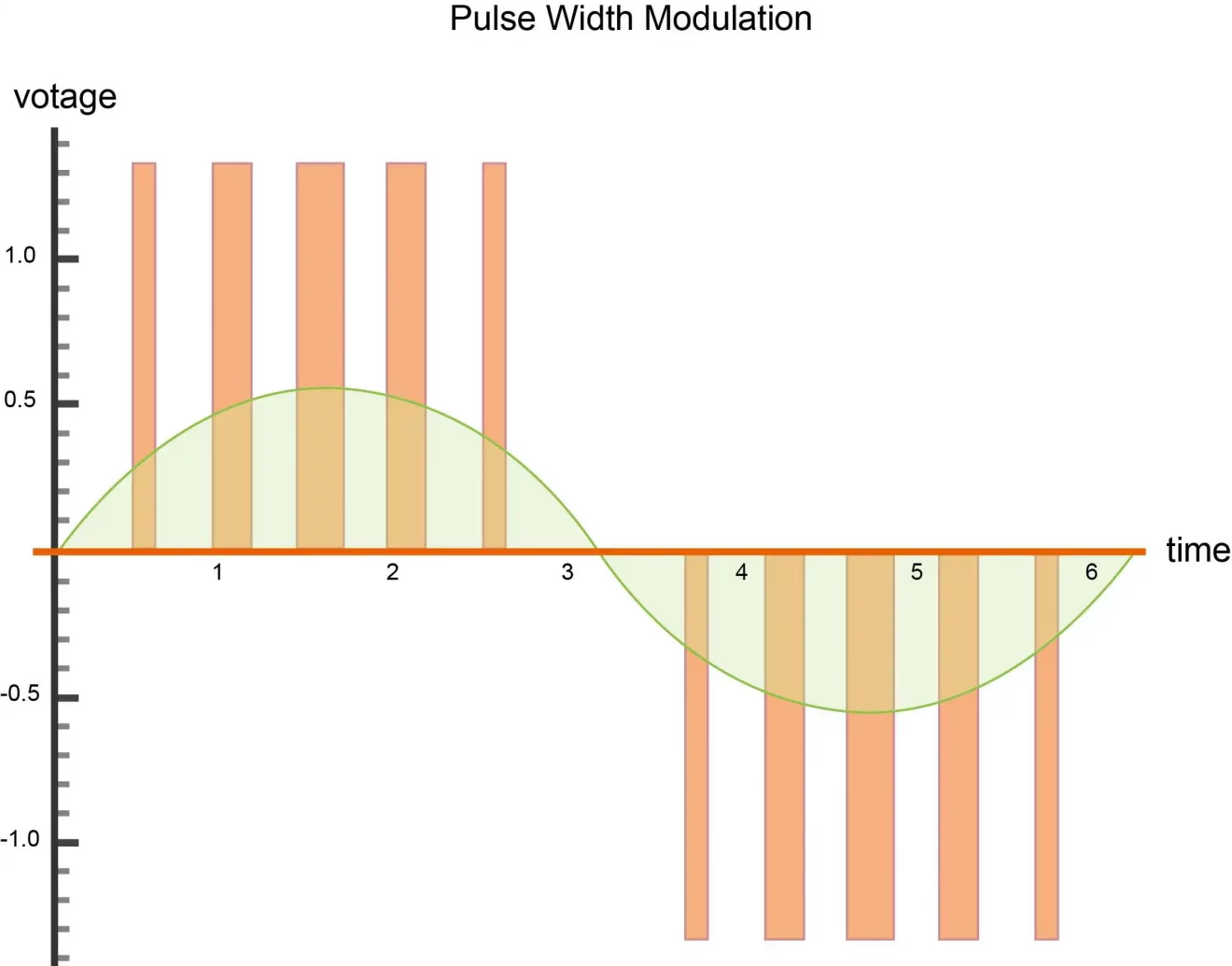
Sine filters are designed to convert the pulse-width modulated (PWM) output of a VFD into a smooth sinusoidal waveform. This reduces motor heating, minimizes audible noise, and extends motor life. Sine filters are ideal for applications requiring precise motor control and low electrical noise, such as in sensitive industrial environments.
2. Output Choke
Output chokes, also known as motor chokes, are used to limit the rate of current rise in the motor windings. They protect the motor from voltage spikes and reduce the stress caused by the VFD’s high-frequency output. Output chokes are particularly useful in long cable runs, where reflected waves can damage motor insulation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right input and output filters for your VFD system is critical for ensuring efficiency, reliability, and longevity. By understanding the options available, you can optimize performance and avoid costly downtime.



