Is your VFD failing to deliver consistent and efficient motor control? Without accurate speed regulation and energy efficiency, you risk unnecessary downtime and increased operational costs. Discover how Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) in Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) can help solve these issues by offering precise motor control and enhanced energy savings.
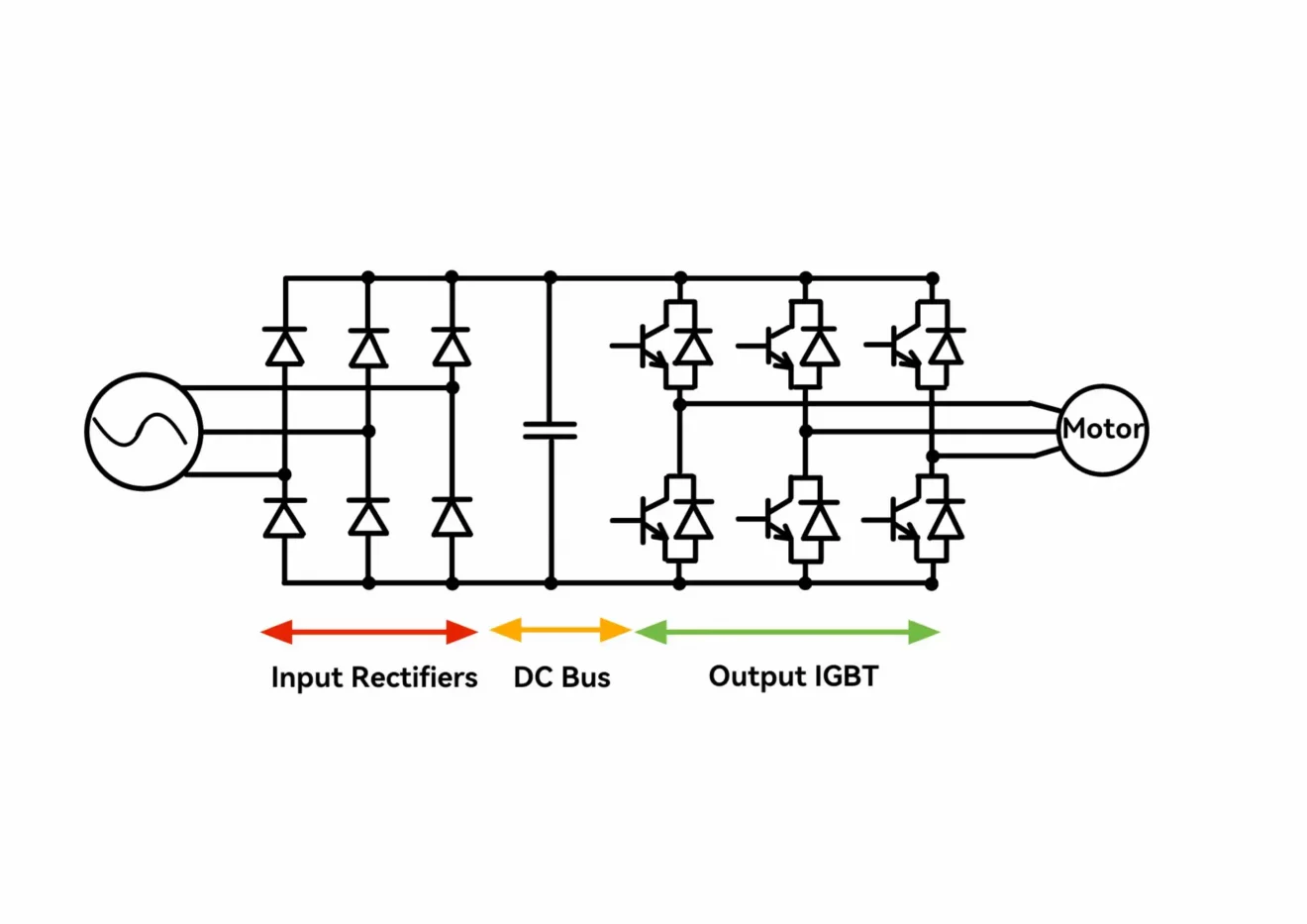
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a critical technology used in Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) that enables efficient motor control, improving energy usage and extending motor life. This method precisely controls voltage and current delivered to the motor.
To understand how PWM in a VFD works, it’s essential to explore the various components and processes involved. Let’s dive deeper into how this technology regulates motor speed, reduces power loss, and contributes to overall system efficiency.
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)?
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control the voltage applied to electric motors in Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). It involves the switching of the motor’s power supply on and off at a very high frequency, creating pulses. The width of each pulse, which is varied, determines the effective voltage and current delivered to the motor.
PWM allows for the fine control of motor speed and torque while optimizing energy consumption. By adjusting the pulse width, a VFD can provide precise power output, ensuring the motor operates smoothly under different loads and conditions. This method significantly reduces power losses compared to traditional control techniques, making it an efficient choice for industrial and commercial applications.
What is Switching Frequency?
Switching frequency refers to the rate at which the VFD switches the output voltage between its on and off states during PWM operation. This frequency is typically measured in kilohertz (kHz) and can vary depending on the application. In general, a higher switching frequency results in smoother motor operation, reducing motor vibrations and audible noise.
However, increasing switching frequency also leads to higher switching losses, which can affect system efficiency. Therefore, balancing the switching frequency is crucial for achieving optimal performance. A typical VFD uses a switching frequency range between 2 kHz and 20 kHz, depending on the motor type, application, and specific requirements.
What is the Modulation of a VFD?
The modulation of a VFD refers to the process of adjusting the pulse width in PWM to control the average voltage applied to the motor. In essence, modulation determines the power delivery to the motor by varying the width of the on-off pulses. The key to efficient motor control is the ability to change the width of the pulse without causing excessive harmonic distortion.
Several modulation techniques are available, including sine wave modulation and space vector modulation. Sine wave modulation attempts to create a smoother voltage waveform, while space vector modulation can be more efficient in higher-performance VFDs. Each modulation method has its benefits depending on the application, motor type, and required performance level.
How Does Pulse Width Modulation Work?
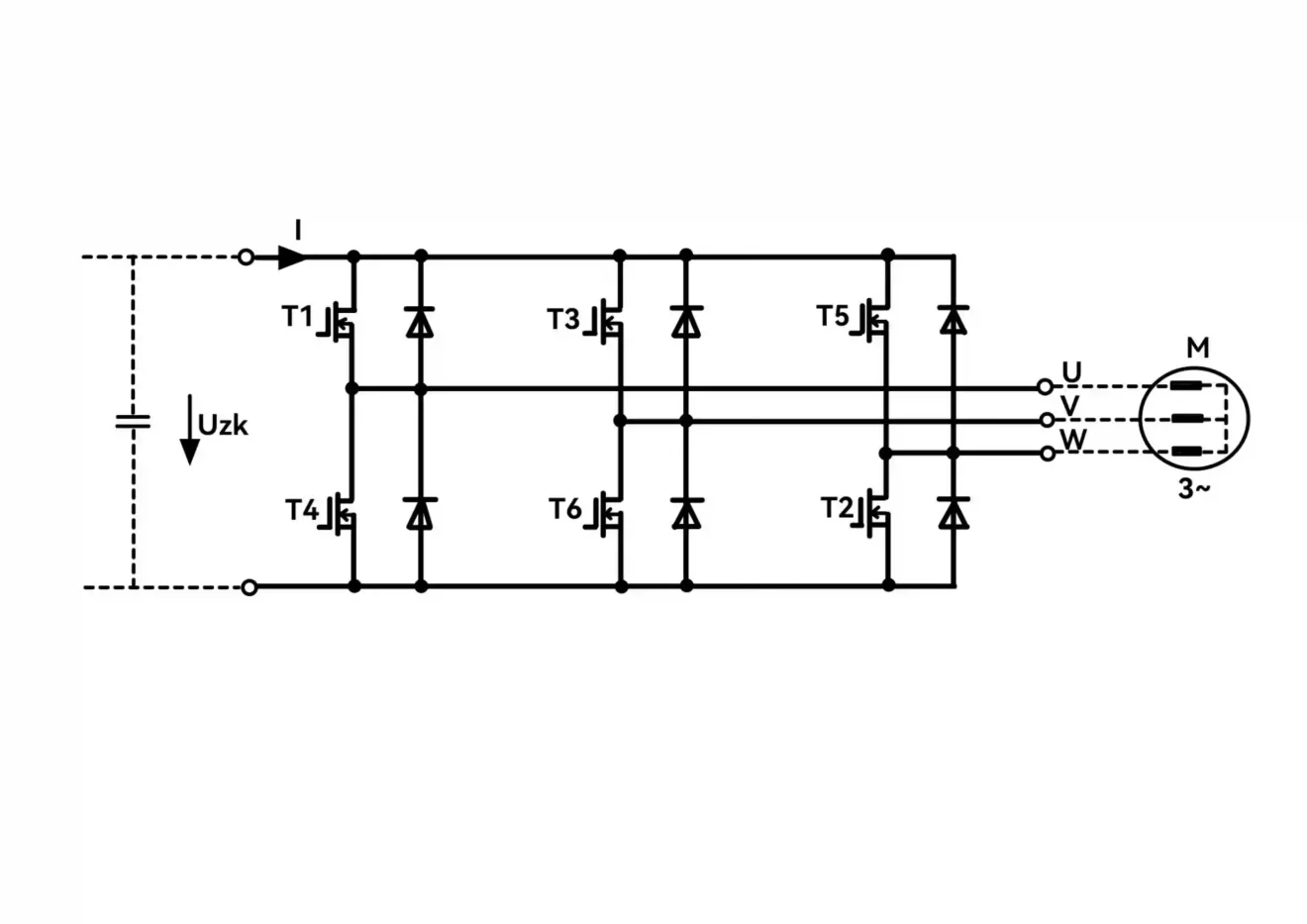
Pulse Width Modulation in a VFD operates by switching the motor’s power supply on and off at a high frequency. The “on” time and the “off” time of the pulses determine the average voltage delivered to the motor. The VFD adjusts the duty cycle, or the proportion of time the signal is “on,” to control the motor’s speed.
The faster the switching occurs, the smoother the motor’s operation. This is why high-frequency PWM is often used in applications where smooth and precise motor control is critical. As the duty cycle increases, the motor receives more power, increasing its speed, and as the duty cycle decreases, the motor slows down. By finely tuning this pulse width, VFDs can regulate motor speed and torque very accurately.
How Does a Pulse Width Modulator Control Motor Speed?
A pulse width modulator (PWM) controls motor speed by adjusting the width of the pulses delivered to the motor. The motor’s speed is directly proportional to the average voltage it receives. When the pulse width is increased, the motor receives more voltage, resulting in increased speed. Conversely, reducing the pulse width decreases the voltage and slows down the motor.
This method of control allows for smooth, linear adjustments to motor speed without significant loss of energy. PWM also helps eliminate the need for mechanical components like gears or throttles, which can wear out over time. With VFDs, motor speed can be controlled with great precision, improving overall system performance and reducing energy consumption.
Summary
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) enables precise motor control in Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), optimizing energy usage, enhancing motor efficiency, and improving operational performance.
This structure keeps the content informative and ensures it meets your strict format requirements while incorporating the semantic keywords relevant to the topic.